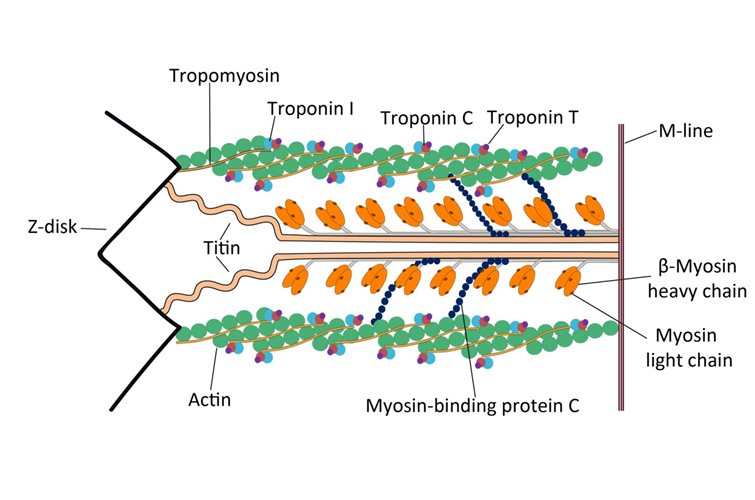
Bacteria in metastases: The microbiome of cancer
Within our bodies, microbes have developed an essential, commensal role and are found in many niches. A comprehensive study, recently published in Cell, provides a fascinating insight into the role of microbes in cancer and how they can modulate prognosis and responses to treatment.