Karyotype vs Array
Karyotype vs Array |
||
|
|
Karyotype |
Array |
| Mosaicism detection |
Individual cells note 1 |
>15-20% of cells |
| Resolution |
10 Mb |
less than 200 kb |
| Copy number detection | Yes |
Yes |
| Balanced translocation detection | Yes |
No |
Note 1 Statistical consideration required. e.g. 20 cell analysis will not always detect 5% mosaicism.
Karyotyping
What is karyotyping?
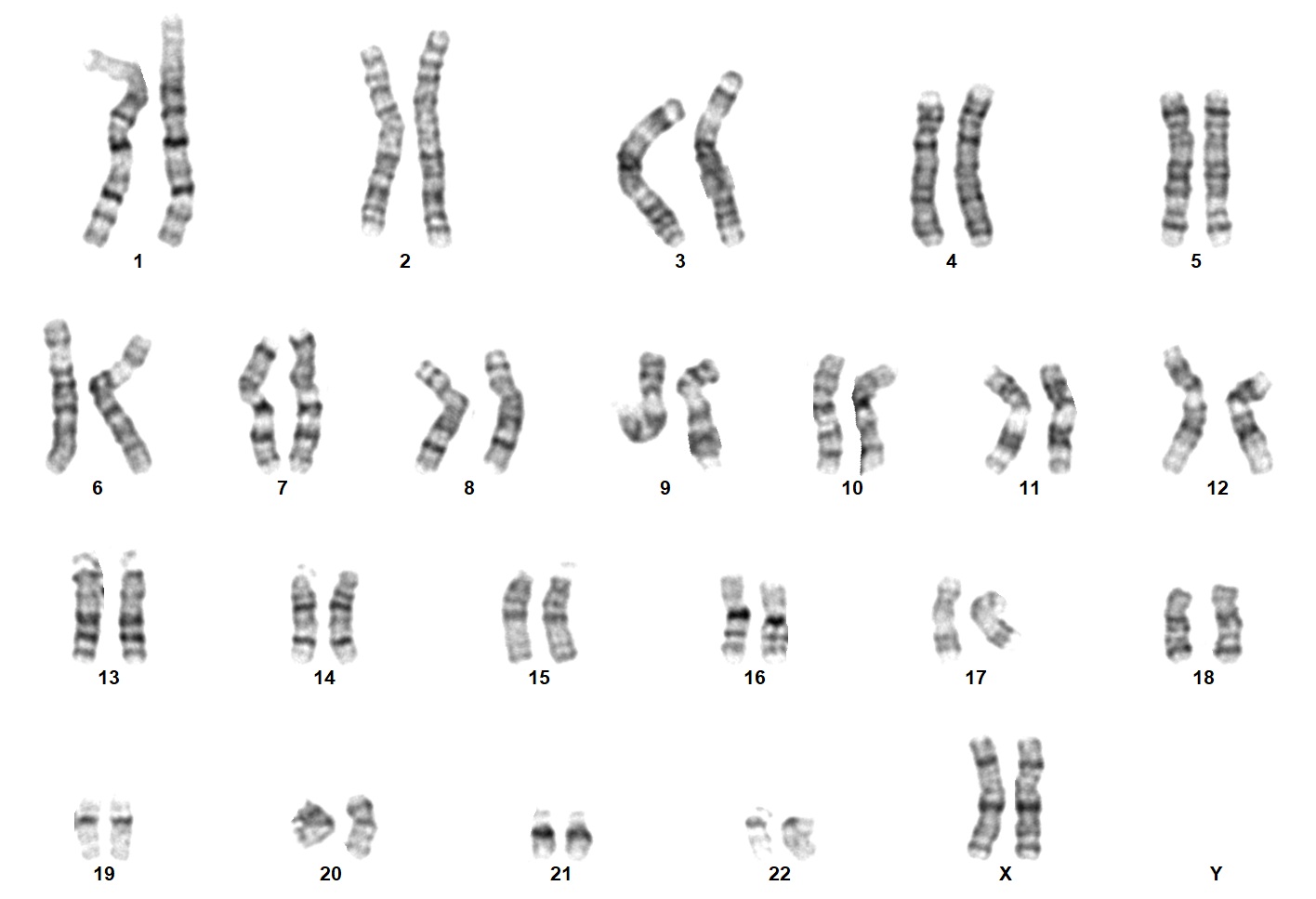
Karyotype analysis is a cytogenetic test that enables the identification of numerical and structural chromosomal abnormalities. Using conventional Giemsa staining techniques, condensed chromosomes are G-banded for observation. Chromosomes are subsequently grouped according to their size, centromere position and banding pattern, and any potential aberrations are identified.
Why karyotyping is important
Karyotyping is the gold standard test required by scientific journals and regulatory agencies to assess the genetic integrity of cells. It is also critical as a regular quality control step to ensure that cells being worked with have not become abnormal. Any abnormality may give rise to altered metabolic and differentiation pathways. Retrospectively discovering that cells are abnormal can invalidate months or years of research. Karyotyping can be used to detect low-level mosaicism and balanced translocations which are easily missed by other methods. Learn more from our webinar.
Karoytpe Service Description
All karyotype services are not the same. At CellGS, skilled, experienced, clinically qualified cytogeneticists working in our Cambridge labs perform the analysis and write insightful reports. We do not rely solely on AI for interpretation. In addition to human and mouse cytogenetic characterisation, we have built up capabilities in a range of other species.
Clinical samples for diagnostic purposes are not accepted.
Common species:
- Human
- Mouse
We also have capabilities for
- Cow karyotyping (bovine karyotyping)
- Pig karyotyping (porcine karyotyping)
- Sheep karyotyping (ovine karyotyping)
- Goat karyotyping (caprine karyotyping)
- Chicken karyotyping (gallus karyotyping)
- Dog karyotyping (canine karyotyping)
- Horse karyotyping (equine karyotyping)
Contact us for further details or if your species isn't listed.
Service levels
We accept 2 types of samples in our laboratories:
- Live cells: cells arrive in culture in a T25 flask (available for UK and Europe only)
- Fixed cells: cells arrive fixed in a 2 mL screwcap tube - we will provide detailed instructions on how to prepare the cells
Please do not send any samples without booking in advance
Number of cells analyzed:
- Normal cells: 20 cells are analyzed per sample as a minimum. This number can be increased to your requirements
- For unstable cancer/highly abnormal samples: sufficient cells will be characterized to identify clonal abnormalities
Reporting times:
- Standard service: 7-10 business days (human or mouse)*
- An Express service is available: please contact us to check availability and turnaround before ordering
*Please note that reporting times may be longer during peak periods. This guidance is for human and mouse. Other species may take longer. You will be advised of any expected delays when placing an order.
Report format
The service results include a descriptive report and at least one publication-quality image of a representative karyotype.
Example Normal Human female from iPS cells
Biosafety level
We can process BSL1 as fixed or live cell samples. We can only process BSL2 samples received as fixed cells.
Array Service Description
What array services do we offer?
The array service from Cell Guidance Systems is offered in the form of Array Genomic Hybridization (AGH).
AGH is performed using Infinium Global Screening Array v3.0: The hybridization data from a single test DNA is compared with a series of control hybridizations in silico. The array has 750,486 distinct features. The AGH assay is particularly useful for assessing acquired loss of heterozygosity (LOH).
AGH platform specifications |
|
| Features |
754,027 |
| Average resolution (median probe spacing) | 2.3 kb |
| Probe size |
50 mer |
| Copy number variation detection? |
Yes |
|
Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) probes |
Millions |
|
Loss of heterozygosity detection? |
Yes |
|
Mosaic detection sensitivity |
>15% |
What types of abnormalities are reported?
Acquired copy number variations (CNVs) and loss of heterozygosity (LOH) present in at least ~15 – 20% of cells will be reported.
For the AGH analysis, an assessment of normal variation is made with reference to ~5,000 normal control samples and a database of ~10,000 clinical samples. However, benign constitutional (heritable) CNVs will not be reported unless requested.
Balanced rearrangements and low-level (10 – 20%) of mosaicism will not be detected using AGH. In practice, this level of mosaicism is statistically similar to the level which can be detected by karyotype analysis of 20 cells.
We recommend array analysis for identifying marker chromosomes and additional material on a chromosome of unknown origin. Karyotype analysis alone can detect certain acquired abnormalities, e.g. gain in the small arm of a chromosome, but the precise nature of certain unbalanced chromosomal abnormalities is difficult to establish by only using G-banding analysis.
Sample types accepted
The array service is only available for human samples. Requirements for the samples are as listed below:
Sample type: isolated DNA
Concentration: >50 ng/µl
Minimum total volume: 1 µg
Purity: A260/A230: 1.8 – 2.2 A260/A280: > 1.8
Report format
A summary report of the results will be issued following completion of the analysis. This will include
- Results Summary - the array profile overview, details of any abnormalities detected, and a description of the analysis carried out
- Result - A handwritten summary of findings
- Karyotype - A technical description of the results
- Test methodology - A description of how the results were generated
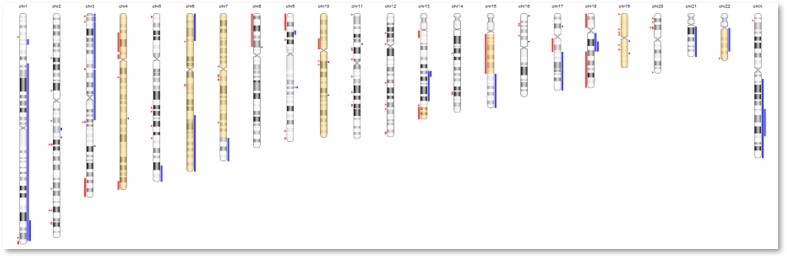
- This will be emailed to you in PDF format, along with a TIFF file containing an image of the genome overview.
The results are returned by email within 15 – 17 business days after the DNA samples have been received at our laboratories. Please note that lead times can be longer during busier periods. If this applies to your order, our team will keep you updated.
Report (Click for PDF)
Ideogram
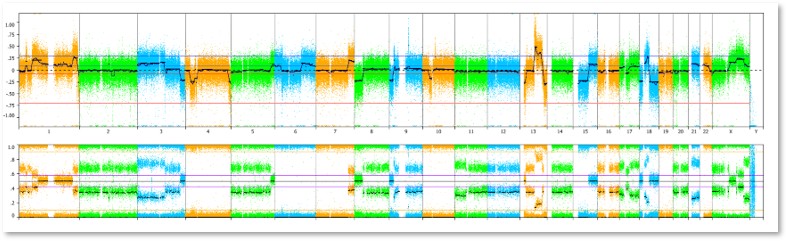
B Allle Frequency plot and LogR ratio plot
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
For any additional questions, please refer to FAQs document here.
Cytogenetics Services Support Literature
Karyotype Analysis
AGH Analysis
Webinar Video
Webinar: Karyotyping iPSCs for chromosomal abnormalities
Cell Guidance Systems’ Cytogenetics team give an overview of the technique of karyotyping and principles used to determine chromosomal patterns and therefore the genetic stability of the cells. They also describe the types of abnormalities that are routinely observed, explain which abnormalities are known to affect cell behaviour, and outline the current recommendations for quality assurance of genetic stability in iPSCs. Published: October 2022
If you have any questions, please contact us by email at [email protected].