Exo-spin™ 96

Product description
Exo-spin™ 96 provides proven size exclusion chromatography (SEC) mini-column (EX01) technology in a 96-well format, allowing up to 96 individual samples to be processed in less than 30 minutes. Sample volumes up to 0.5 ml can be purified.
The kit provides flexibility with 8-column strips detachable from the plate, so you can process 8 samples in 8-column strips if needed
The Exo-spin™ 96 well product offers:
- High-throughput exosome isolation at the benchtop in the standard 96 well format in under 30 minutes
- Purify up to 0.5 ml of each sample
- Up to 99% of free proteins removed
- Outstanding reproducibility +/- 5% Standard deviation, for consistent exosome purification, time after time
- Flexibility to just work with single strips of 8 columns at a time
- The convenience of purified exosomes eluted directly into a 96 well plate ready for high throughput downstream applications
-
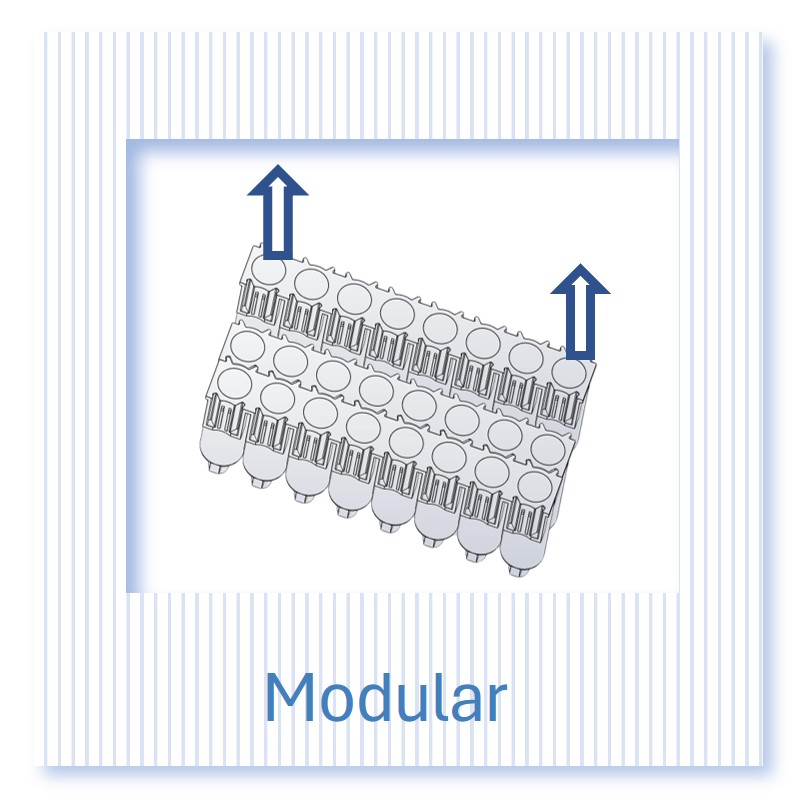
The Exo-spin™ 96 can be used to isolate exosomes directly from protein-rich samples such as sera and plasma. If required, you can concentrate the sample with your preferred concentration method (e.g. concentrator, precipitation buffer) to isolate from large volumes of low-protein biofluids, such as cell culture medium, cerebral spinal fluid (CSF), and urine.
The EX07 Exo-spin™ kit has been developed to process up to 500 µl blood samples (plasma or sera) using iterative loading
Exo-spin™ 96 column - maximum sample loading |
||||
|
Precipitant/concentration |
no |
yes |
no |
yes |
|
Iterative loading |
no |
no | yes |
yes |
|
Sera and plasma |
100 µl |
500 µl |
500 µl |
2500 µl |
|
culture media, urine, saliva |
100 µl |
50 ml |
500 µl |
250 ml |
Table 1. The maximum sample size that can be loaded onto a column will depend on the sample type and whether the sample is concentrated by precipitation or loaded iteratively.
Exo-spin™ column capacity
100 µl of the sample may be loaded onto each column. Iterative loading allows up to 0.5 ml sera in total to be purified.
Exo-spin™ resin pore size
The pore size within the resin is approximately 30 nm. Free molecules (e.g. proteins, lipids) which are smaller than 30 nm will enter into the pores within individual resin beads, and their movement through the column is slower.
Highest recovery and purity
Blood plasma and sera typically contain around 1 x 1012 exosomes/ml. Size exclusion chromatography (SEC), provides a superior technique to purify exosomes from blood. Samples can be added directly onto the column or concentrated, if required, prior to application. Exosomes in a range of 30-200 nm will elute in the first fraction. 99% of free, non-exosomal proteins and lipids will be retained in the column and will elute later than the exosomes, ensuring a highly pure sample ready for downstream application.
Reproducibility
Reproducible purification provides the starting point to reproducible data. Exo-spin™ 96 columns provide excellent reproducibility with a standard deviation for exosome yield of just 5%. All Cell Guidance Systems columns are manufactured in our own manufacturing facility using advanced production techniques and quality control systems. This ensures the high reproducibility between each and every column within and between purification plates. A large number of peer-reviewed scientific papers have been published describing research that has been enabled by the use of Exo-spin™.
Storage
Upon receipt, store the kit at 4°C.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
For any additional questions, please refer to the FAQs document below.
If you are just starting to work with exosomes, you may wish to consider our starter pack
We designed the ideal starter pack to guide your exosome research. The starter pack includes the exosome purification kit of your choice, exosome validated antibodies and NTA profiling analysis. Complete details can be found in the product page here.
Watch how easy it is to purify a large number of exosome samples with Exo-spin™ 96
Product data
Exo-spin™ comparative data
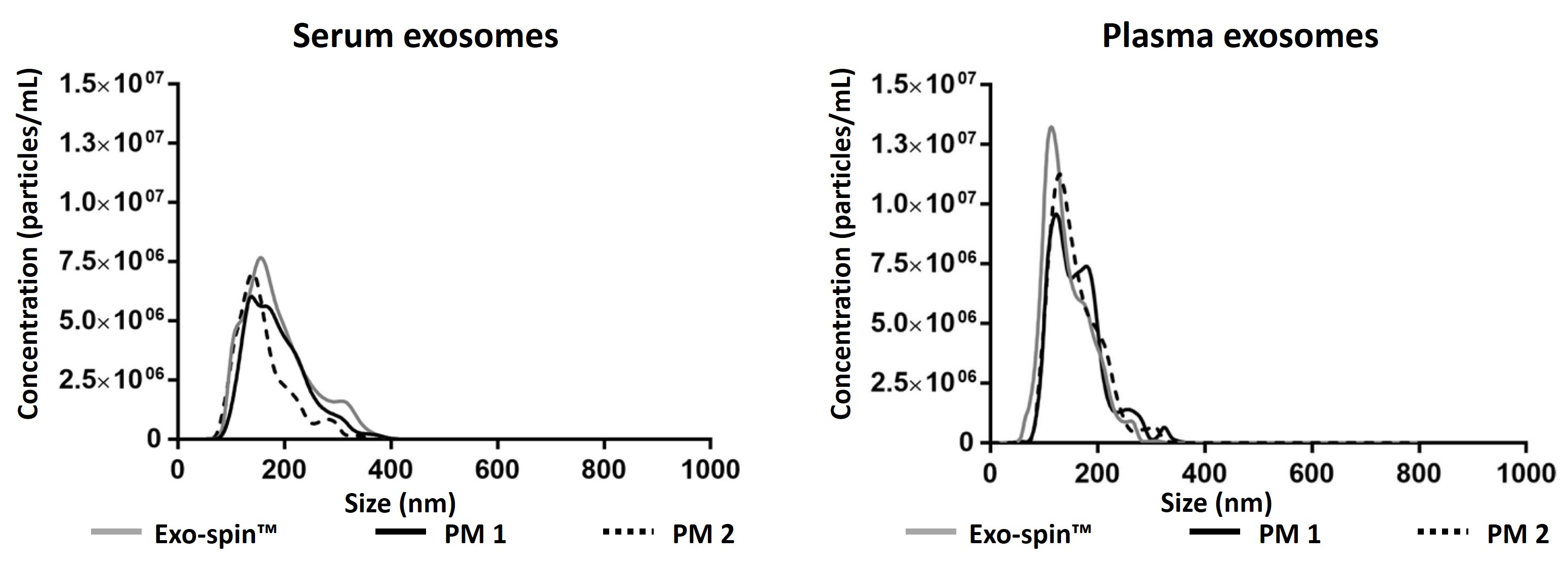
Exo-spin™ shows superior yield and purity. Data determined by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). Each curve represents the average of 3 technical replicate measurements for each exosome isolation method and biofluid triplicate experiment. (PM = Precipitation Method). Data generated for Exo-spin mini columns which have the same resin and measurements as Exo-spin 96. Adapted from (Martins, TS et al., 2018).
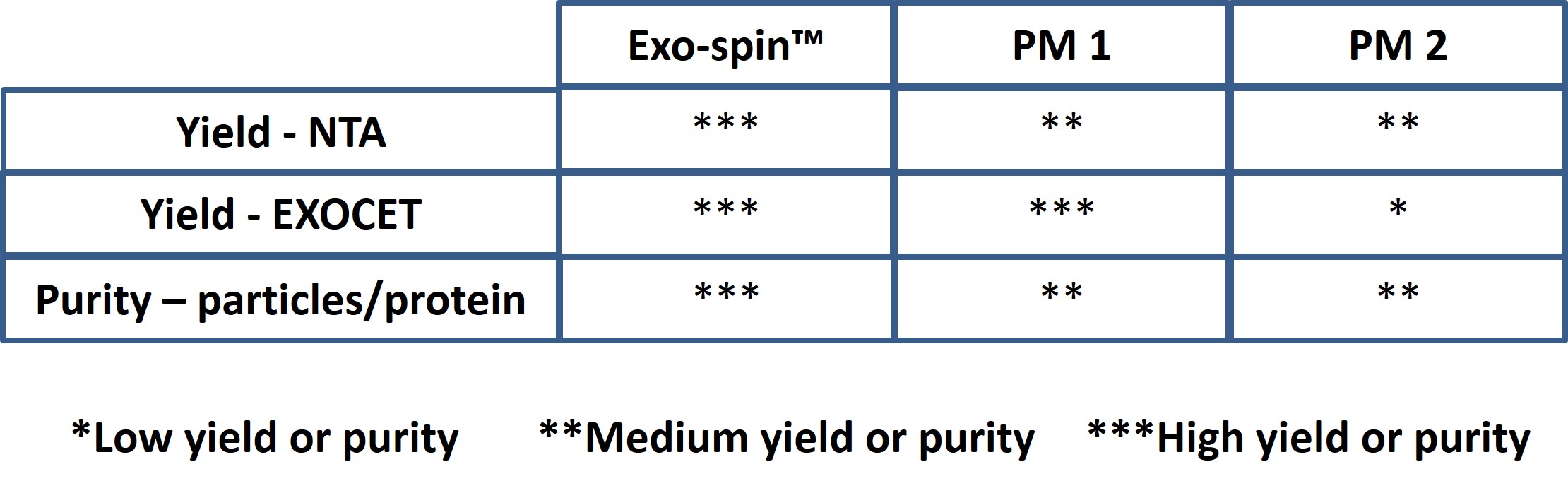
Data determined by NTA and EXOCET. Serum sample has been analysed for qualitative comparison between Exo-spin™ and precipitation methods.
Characterizing Exo-spin™ 96 isolated exosomes
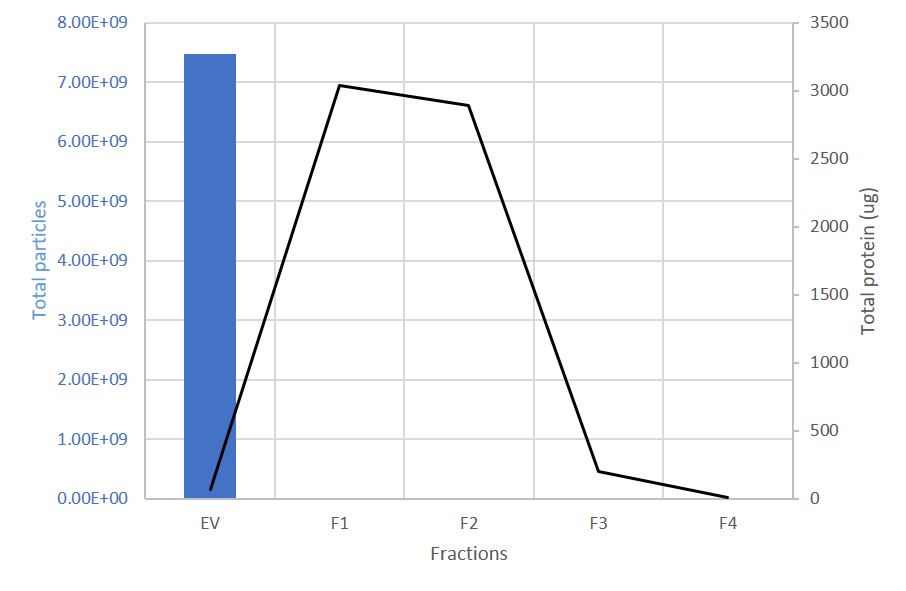
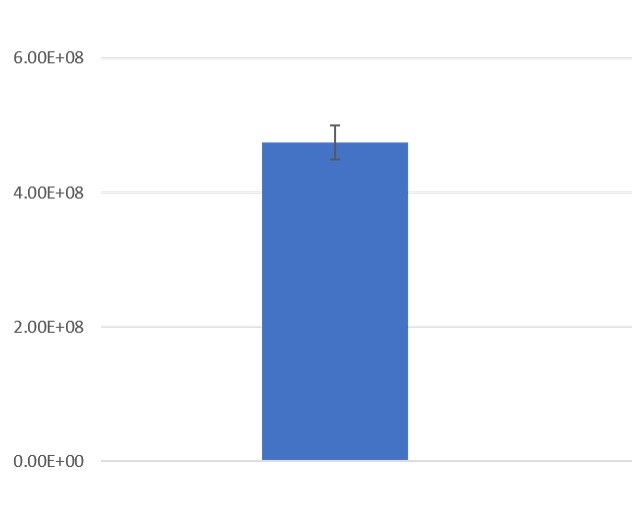
EV and protein content in fractions collected from columns. The first fraction (EV) containing the exosomes is retained. 99% of proteins are present in the subsequent, discarded fractions (F1-F4).
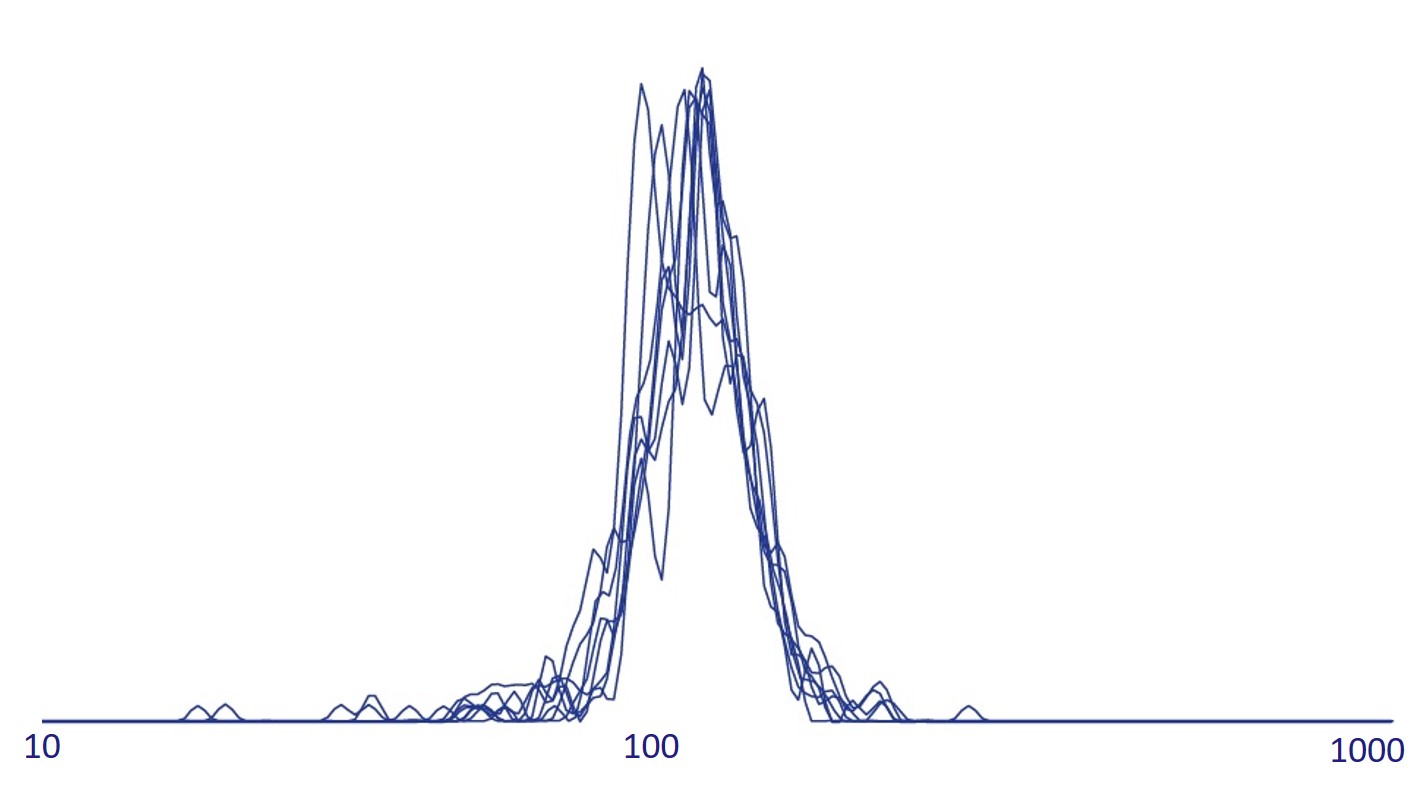
Exosome characterization with NTA. Excellent reproducibility is routinely achieved. Data for 8 columns shown. Exosomes have been isolated using Exo-spin™ 96 and analysis performed with the ZetaView® instrument.
Downstream applications: advice and content
The EX07 Exo-spin™ 96 kit is compatible with all downstream applications. The column characteristics of this kit are identical to EX01 Exo-Spin™ which has been used in a wide range of different applications. A few examples are provided below.
RNA analysis:
- Wang L., Wang C., Jia X. and Yu J. (2018). Circulating Exosomal miR-17 Inhibits the Induction of Regulatory T Cells via Suppressing TGFBR II Expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry; 50:1754–1763.
- Emanueli C., Shearn AI., Laftah A., Fiorentino F., Reeves BC., Beltrami C., Mumford A., Clayton A., Gurney M., Shantikumar S. and Angelini G. (2016). Coronary Artery-Bypass-Graft Surgery Increases the Plasma Concentration of Exosomes Carrying a Cargo of Cardiac MicroRNAs: An Example of Exosome Trafficking Out of the Human Heart with Potential for Cardiac Biomarker Discovery. PLoS One 29;11(4):e0154274.
Mass Spectrometry:
- Menezes-Neto A., Fidalgo Sáez MJ., Lozano-Ramos I., Segui-Barber J., Martin-Jaular L., Estanyol Ullate JM., Fernandez-Becerra C., Borrás FE., and del Portillo HA. (2015). Size-exclusion chromatography as a stand-alone methodology identifies novel markers in mass spectrometry analyses of plasma-derived vesicles from healthy individuals. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles; 4: 10.3402/jev.v4.27378.
Functional study:
- Sheller-Miller S, Trivedi J, Yellon SM, and Menon R. (2019). Exosomes Cause Preterm Birth in Mice: Evidence for Paracrine Signaling in Pregnancy. Scientific Reports 24;9(1):608.
Further resources:
Please see the Exosome Resources Page
Citations
There are more than 800 citations for Exo-spin products