Exo-spin™ mini-HD
Product description
Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) columns are a reliable method for exosome isolation and can be used as a stand-alone product or as part of a combined strategy for isolating small EVs.
The EX05 Exo-spin™ kit contains packed and equilibrated ready-to-use SEC columns.
Products on this page contain Exo-spin™ mini-HD columns
Exo-spin™ mini-HD column - maximum sample loading |
||||
|
Precipitant/concentration |
no |
yes |
no |
yes |
|
Iterative loading |
no |
no | yes |
yes |
|
sera and plasma |
150 µl |
750 µl |
750 µl |
3750 µl |
|
culture media, urine, saliva |
150 µl |
75 ml |
750 µl |
375 ml |
Table 1. The maximum sample size that can be loaded onto a column will depend on the sample type and whether the sample is concentrated by precipitation or loaded iteratively.
Why should I consider Exo-spin™ mini-HD?
The EX05 Exo-spin™ kit has been developed to purify exosomes from intermediate volumes, complementing the range of exosome isolation solutions.
- High-resolution protocol to optimize yield and purity and enable finer fraction collections
- Robust, simple, quick, and economical
- SEC method for excellent exosome recovery
Exo-spin™ column and resin pore size
The column bed volume is 3.5 ml, allowing for 150 µl of volume to be loaded on top of the column.
The pore size of the resin is approximatively 30 nm to attain a highly pure exosome elution. All other molecules (e.g. proteins, lipids) which are smaller than 30 nm will enter into the pores and remain trapped in the column.
Fractionation analysis
The Exo-spin™ mini-HD columns allow a high-resolution fractionation protocol operated by gravity, no special equipment is required.
Highest recovery and purity
As mentioned above, essentially all proteins and lipids will be retained in the column and will elute later than the exosomes, ensuring a highly pure sample ready for your downstream application. A concentration step might be needed prior to SEC isolation depending on your sample type, we offer a precipitation buffer that can be purchased separately (cat code EX06).
Reproducibility
All our columns are manufactured in our laboratory to ensure a high reproducibility between each lot. As proof of reproducibility and batch-to-batch consistency, a large number of peer-reviewed scientific papers have been published describing the use of Exo-spin™.
Storage
Upon receipt, store purification columns at 4°C.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
For any additional questions, please refer to FAQs document below.
Start today - Select our starter pack
We designed the ideal starter pack to guide your exosome research. The starter pack includes the exosome purification kit of your choice, exosome validated antibodies, and NTA profiling analysis. The complete details can be found in the product page here.
Product data
EX05 Exo-spin™ mini-HD columns data
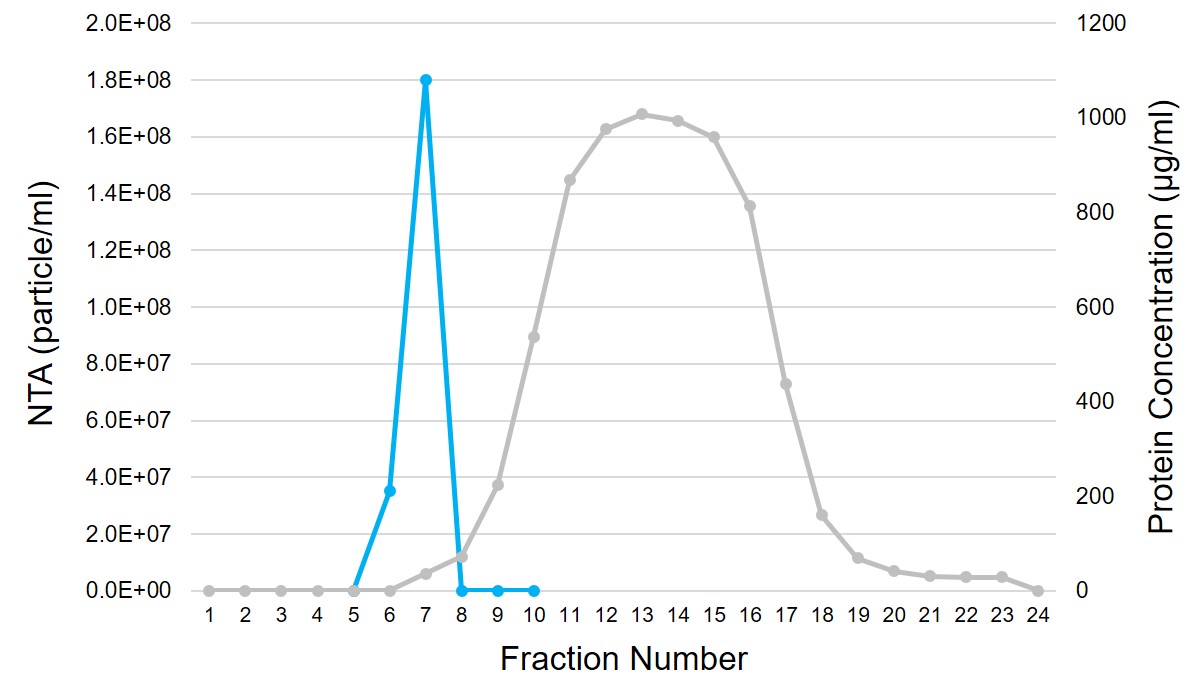
Human serum fractionation profile using Exo-spin™ mini-HD. 100 µl of human serum was added to the Exo-spin™ mini-HD column. The protein concentration (grey) was estimated by Bradford assay and the particle concentration (blue) was measured by NTA using ZetaView® instrument from Particle Metrix.
If you would like more information on the exosome extraction profile using Exo-spin™ mini-HD columns, please refer to the EX05 user guide below in the documents section.
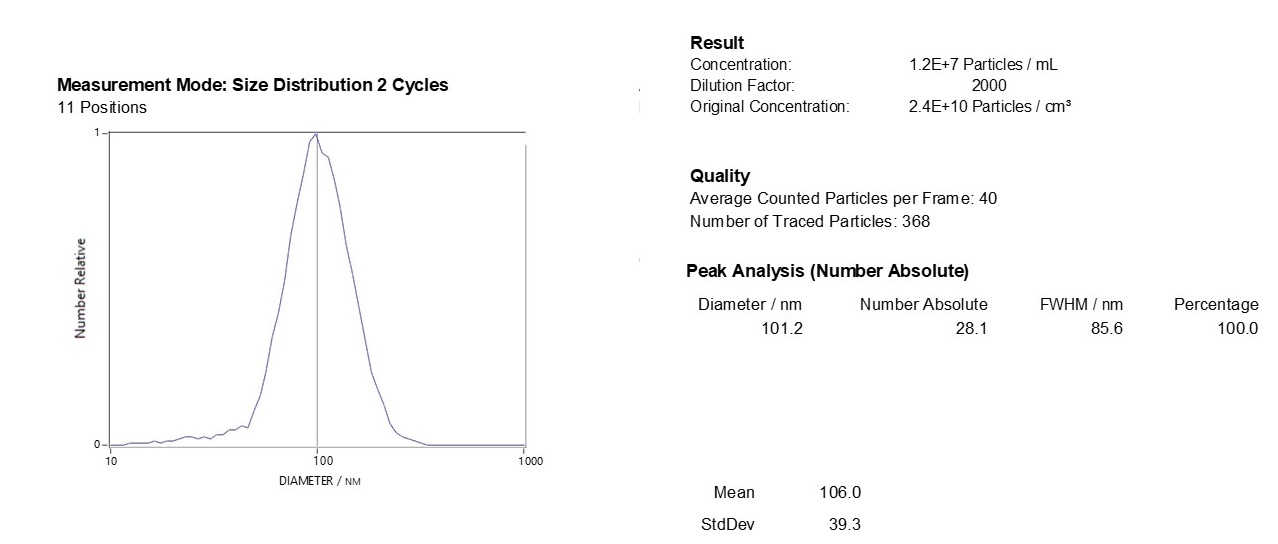
Characterizing Exo-spin™ isolated exosomes using nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA)
Exosome characterization with NTA. Exosomes have been isolated using the Exo-spin™ kit and analysis performed with the ZetaView® instrument.
Downstream applications: advice and content
The Exo-spin™ kits are compatible with all downstream applications and have been cited in a large range of different applications.
RNA analysis:
- Santangelo L, Giurato G, Cicchini C, Montaldo C, Mancone C, Tarallo R, Battistelli C, Alonzi T, Weisz A and Tripodi M. (2016). The RNA-Binding Protein SYNCRIP Is a Component of the Hepatocyte Exosomal Machinery Controlling MicroRNA Sorting. Cell Reports 17(3):799-808.
- Brook AC, Jenkins RH, Clayton A, Kift-Morgan A, Baby AC, Shephard AP, Mariotti B, Cuff SM, Bazzoni F, Bowen T, Fraser DJ, and Eberl M. (2019). Neutrophil-derived miR-223 as local biomarker of bacterial peritonitis. Scientific Reports 9(1):10136.
Immunoassay:
- Salimu J, Webber J, Gurney M, Al-Taei S, Clayton A and Tabi Z. (2017). Dominant immunosuppression of dendritic cell function by prostate-cancer-derived exosomes. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles 6(1):1368823.
Exosome engineering for therapeutic cargo:
- Kojima R, Bojar D, Rizzi G, Hamri GC, El-Baba MD, Saxena P, Ausländer S, Tan KR and Fussenegger M. (2018). Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson's disease treatment. Nature communications 9: 1305.
Functional study:
- Piao YJ, Kim HS, Hwang EH, Woo J, Zhang M and Moon WK. (2017). Breast cancer cell-derived exosomes and macrophage polarization are associated with lymph node metastasis. Oncotarget 9(7): 7398–7410.
Proteomic (MS/MS analysis):
- E L Kavanagh, S Lindsay, M Halasz, L C Gubbins, K Weiner-Gorzel, M H Z Guang, A McGoldrick, E Collins, M Henry, A Blanco-Fernández, P O' Gorman, P Fitzpatrick, M J Higgins, P Dowling, and A McCann. (2017). Protein and chemotherapy profiling of extracellular vesicles harvested from therapeutic induced senescent triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncogenesis 6(10): e388.
Protein assay:
- Welton JL, Webber JP, Botos LA, Jones M and Clayton A. (2015). Ready-made chromatography columns for extracellular vesicle isolation from plasma. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles 4:27269.
Further resources:
Please see the Exosome Resources Page
Citations
There are more than 800 citations for Exo-spin products