Domestic central heating vs Human circulation

From pressure regulation to valves, and balanced distribution; the domestic plumbing system and the human circulatory system share a surprisingly wide range of similarities. There are of course key differences in scale and function. For example, heating only has the job of generating and distributing heat. In contrast, the function of circulation, supplying the myriad needs of tissues, is much more complex. Notwithstanding, the design of heating systems and the evolution of human circulation have arrived at a remarkably similar set of solutions. Perhaps heating engineers were inspired by human biology!?
Component Parts
Pipes and Vessels
In plumbing, pipes are used to transport water throughout a building, similar to how blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries) transport blood throughout the body.
Pumps
The heart acts as a pump in the circulatory system, pushing blood through the vessels. Similarly, plumbing systems use pumps to move water through pipes.
Heater unit vs Lungs
Heating systems are designed to distribute heat introduced by heating water in a boiler. A primary function of human circulation is to distribute oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide with exchange of these occurring in the lungs.
Valves
Both systems use valves to control the flow of fluids. In plumbing, valves can stop or redirect water flow, while in the circulatory system, valves in the heart and veins ensure that blood flows in the correct direction.
Pressure Regulation
Both systems require pressure regulation to function properly. In plumbing, water pressure must be maintained to ensure water reaches all parts of a building. In the circulatory system, blood pressure is regulated to ensure that blood reaches all tissues and organs.
Distribution Network
Both systems have a network that distributes the fluid to various locations. In plumbing, this means delivering water to radiators which have are designed to efficiently transfer heat to rooms. In the circulatory system, blood is distributed to different organs and tissues throughout the body via capillaries designed to transfer nutrients and waste products between the cells and blood.
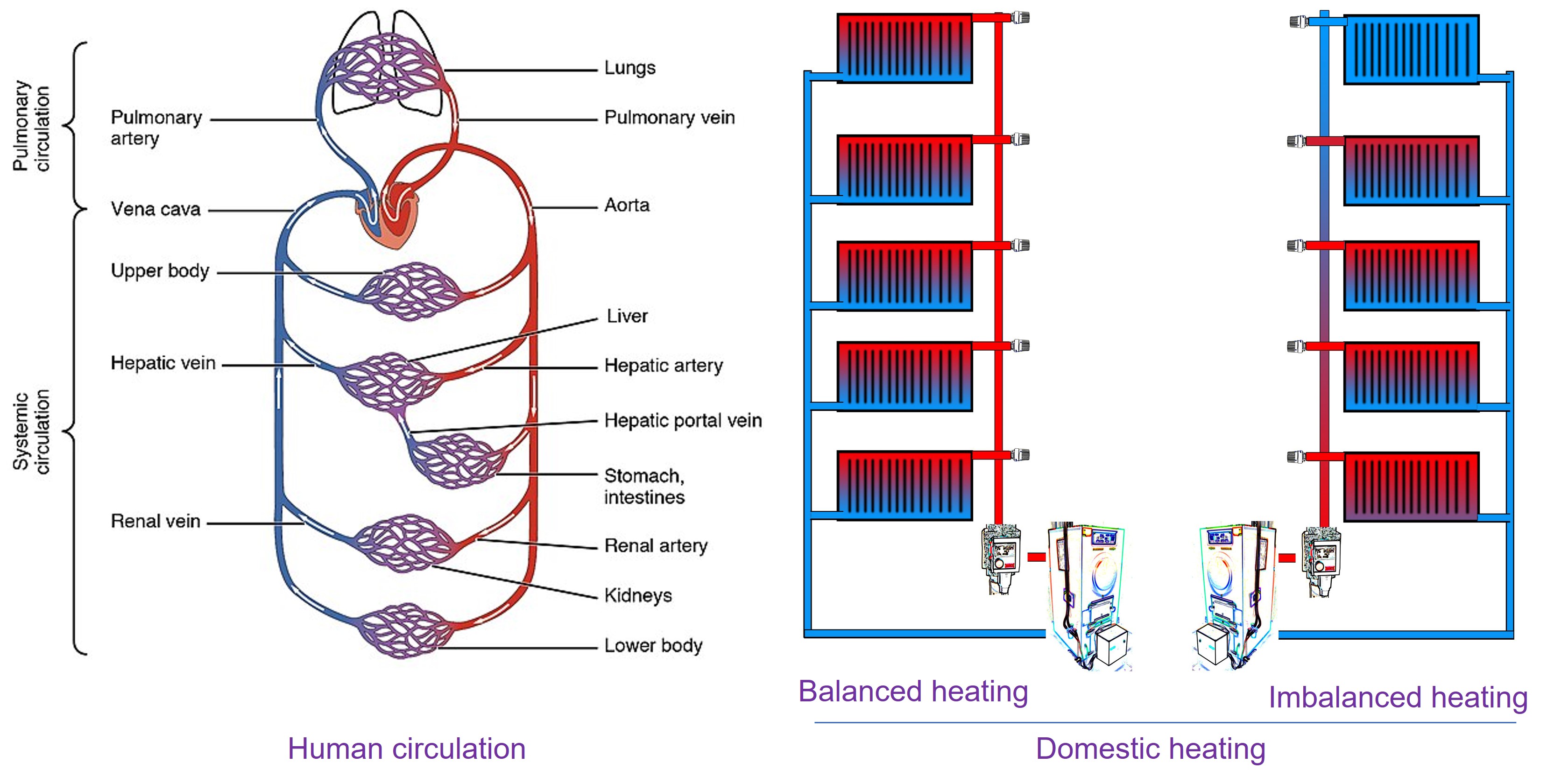
Similarities between human circulation and a domestic heating system. Image credits: Human circulation. Heating
Maintenance and Faults
Both systems require regular maintenance to function properly. Plumbing systems need to be checked for leaks, blockages, and corrosion, while the circulatory system requires a healthy lifestyle to prevent issues like atherosclerosis or hypertension. It may be possible to repair blockages with surgery such as the introduction of stents.
Imbalanced circulation is a problem in both systems. In Plumbing, imbalanced water pressure where too much water is flowing through a rator to the return stream (see the bottom radiator in the unbalanced heating system above) can lead to problems such as insufficient water flow to certain areas, leaks, or even burst pipes. It can also cause uneven distribution of hot and cold water, leading to discomfort and inefficiency. In the Circulatory System:, imbalanced circulation can lead to various health issues. Poor circulation can result in symptoms like cold extremities, fatigue, and swelling. It can also lead to more serious conditions such as varicose veins, blood clots, or even heart failure if the underlying causes are not addressed. Imbalanced circulation in the body can be due to factors such as blockages in the arteries (atherosclerosis), heart problems, or issues with blood pressure regulation.
In both systems, addressing imbalances is crucial for optimal function. For plumbing, this might involve adjusting pressure settings, repairing leaks, or clearing blockages. For the circulatory system, it may involve lifestyle changes, medication, or medical procedures to improve blood flow and heart function.
Overall, maintaining balance and proper flow in both systems is essential for their efficient operation and to prevent potential problems are there human conditions when there is too much blood flow to a region or organ, that leads to reduced flow to other areas?
What are medical conditions caused by excessive flow to organs?
There are several medical conditions where excessive blood flow to one region or organ can lead to reduced blood flow to other areas. This imbalance can cause various health issues. Examples include:
Hyperemia
This is a condition where there is an excess of blood in the vessels supplying an organ or tissue. It can be active (due to increased blood flow) or passive (due to impaired venous return). While hyperemia itself is not always harmful, it can lead to congestion and affect blood flow to other areas.
Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs)
These are abnormal connections between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. AVMs can lead to increased blood flow to the affected area, potentially depriving surrounding tissues of adequate blood supply.
Steal Syndrome
This occurs when blood is “stolen” from one area to supply another, often due to the presence of a vascular access point like a dialysis fistula. It can lead to reduced blood flow and ischemia in the area from which blood is diverted.
Compartment Syndrome
Although primarily a condition of increased pressure within a muscle compartment, it can lead to reduced blood flow to the affected area and surrounding tissues. This can result in tissue damage and requires prompt medical intervention to restore normal circulation.
Tumors
Some tumors can create their own blood supply through a process called angiogenesis, leading to increased blood flow to the tumor. This can sometimes divert blood away from surrounding tissues, potentially causing ischemia or nutrient deprivation in those areas.
Inflammation
Inflammatory processes can lead to increased blood flow to the affected area as part of the body’s immune response. While this is a normal part of healing, excessive or chronic inflammation can lead to imbalances in blood distribution.
Vasodilation
Conditions that cause widespread vasodilation (such as septic shock or anaphylaxis) can lead to pooling of blood in certain areas, reducing effective circulation to vital organs and tissues.
In all these cases, the imbalance in blood flow can lead to complications if not managed properly. Medical intervention may be necessary to restore balanced circulation and ensure that all tissues and organs receive adequate blood supply.
IMAGE Wikimedia commons
Learn more about powerful technologies that are enabling research: