Exosome therapeutics in development for treating Covid
Times of crisis can precipitate rapid technological development and the Covid-19 crisis is presenting an opportunity for new therapeutic modalities. Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna’s Covid vaccines which both rely on RNA have been ground-breaking. Could Covid-19 also clear the path for the first exosome therapeutics?
A clear end to the Covid-19 pandemic is no yet in sight and may not be achievable. Vaccine coverage will remain patchy and the emergence of vaccine-resistant virus variants suggests that the virus will become endemic.
Fortunately, we are not wholly reliant on vaccines to combat this virus. Effective therapeutics such as dexamethasone and tocilizumab as well as improved patient management strategies have emerged. Many drugs are being evaluated under the Recovery Trial program. The odds of survival for severe Covid patients are much greater now than a year ago.
If, as seems likely, complete eradication of Covid is not possible, therapies are needed to further reduce mortality and mitigate the effects of long-Covid. The causes of death for most Covid patients are acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and sepsis. ARDS is results from alveolar collapse associated with inflammation caused by high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines released in response to the infection.
Six ongoing clinical trials using exosomes as the therapeutic modality to treat Covid-19 include:
CD24 to reduce cytokine release. Aerosol delivery. Ichilov medical centre, Tel Aviv, Israel. Phase I
The Times of Israel reported a Phase 1 clinical trial in which 29/30 patients with severe or moderate Covid were discharged from hospital with 5 days.
MSC-derived exosomes to reduce cytokine release.
MSCs are frequently used in cellular therapies including dozens of trials for Covid. Unsurprisingly, MSCs are also frequently used as a source of therapeutic exosomes which have attracted interest for their ability to suppress inflammation. Three ongoing studies are using mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) exosomes
Kimera Phase I IND filing
Samara Regional Medical Centre Dynasty (Russian Government Sponsored). Phase I
In addition BrainStorm. is at a pre-clinical stage to use MSC exosomes for Covid therapy
Covid-19 donor activated T cells secreting exosomes including IFN-gamma. Kayseri, Turkey
Aerosol application to treat early stages of coronavirus pneumonia. The exosomes are derived from T-cells isolated from Covid patients. IFN-gamma is amongst the cargo proteins generated by these cells. The clinical trial is expected to complete in May 2021.
CAP-1002 cardiosphere-derived cells release exosomes that modulate inflammatory cytokines. Capricor Therapeutics
Cardiospheres (CSs) are self-assembling multicellular clusters from the cellular outgrowth from cardiac explants cultured in nonadhesive substrates. CS-derived exosomes have been reported to have anti-inflammatory properties. Positive effects reported in a small number of acute patients for compassionate use – not a formal clinical trial. Capricor Therapeutics has gained IND approval from the FDA.
Zofin: Human Amniotic fluid derived exosomes, minimally manipulated. Intravenous administration. Phase I. Organicell
Zofin is an acellular, minimally manipulated product, derived from human amniotic fluid (HAF). Zofin “contains over 300 growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines as well as other extracellular vesicles/nanoparticles derived from amniotic stem and epithelial cells.” Zofin has demonstrated therapeutic potential based on suppression of cytokine activation.
ExoFlo: bone marrow derived extracellular vesicles. Phase II. Direct Biologics.
Covid patients treated as part of an ongoing Phase II study of lung disease in inflammation. There are few other details in the FDA submission
In addition to these experimental therapies which have made it to clinical trials, there are many alternative approaches to using exosomes to treat Covid which haven’t yet reached the clinic.
Perhaps the most exciting result to emerge so far using exosomes to treat Covid is from the group in Tel Aviv. We await the details in a peer-reviewed paper. A potential issue with exosome-based therapies is scalability. Techniques used in the lab and for clinical trials to purify exosomes may not be viable for large-scale manufacturing to treat large numbers of patients.
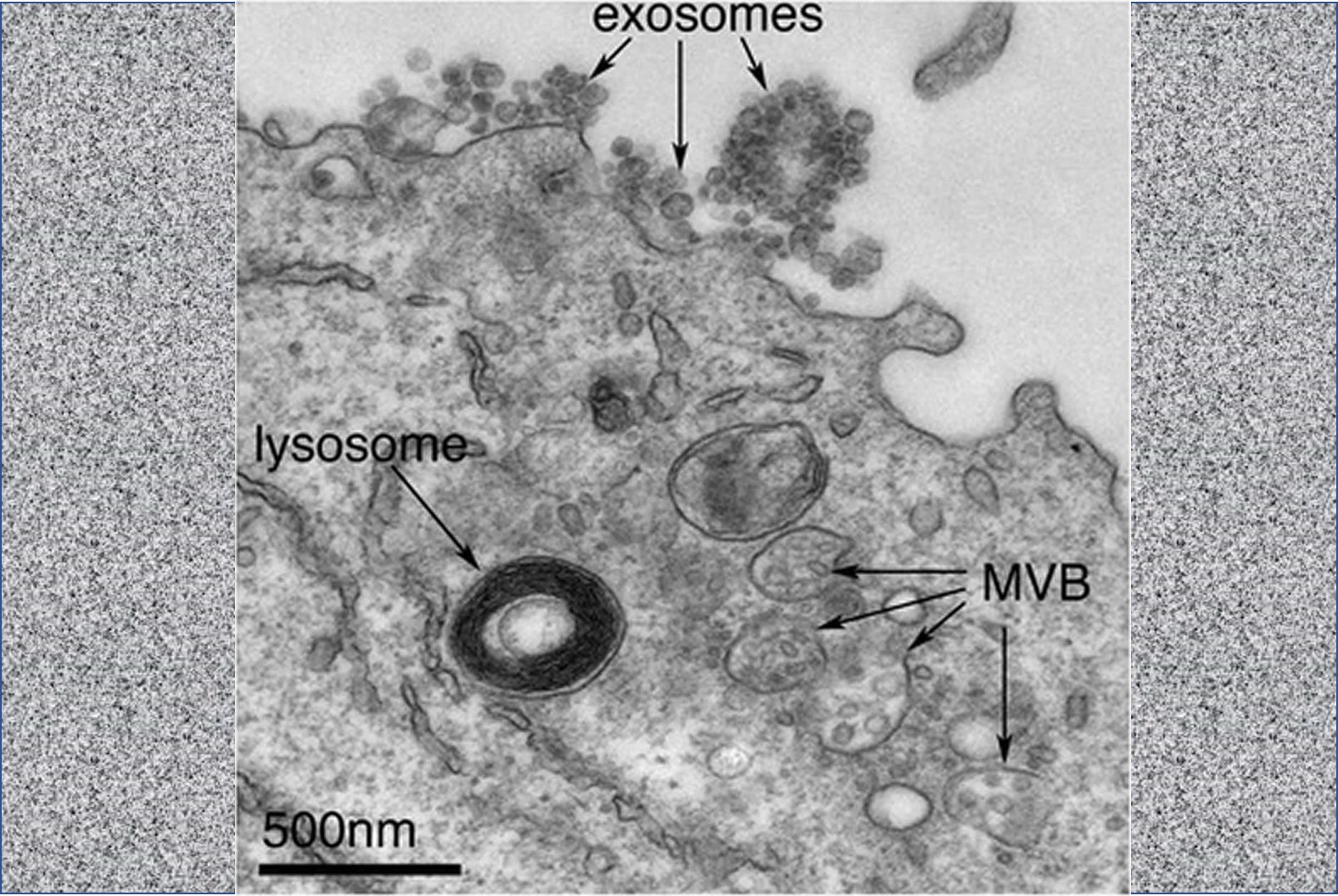
IMAGE: Budding exosomes, James Edgar, CC

