Hepatathletes: Alpha 7 hydrogel boosts hepatocytes' all round performance

Cultured hepatocytes are critical for drug toxicity testing but are not able to maintain their performance levels for long. A new hydrogel is set to improve durability, turning laggard cells into winning performers.
The importance of hepatocytes in drug development
Liver failure caused by off-target drug effects is one of the major pitfalls of drug development. Comprehensively testing a candidate drug’s effect in animal models and against liver cells in vitro is an essential and costly aspect of the drug development process. Consequently, hepatocytes are one of the most important cell types used in drug development. Using hepatocytes, the function of enzymes that metabolize compounds in the liver is tested. Primary human hepatocytes, available from Cell Guidance Systems, directly harvested from human livers prior to use, provide a gold standard. However, the utility of these cells is ephemeral leaving a short window of opportunity to perform an assay.
Hydrogels can improve hepatocyte performance
To improve the relevance and accuracy of cell culture-based assays, there has been a general movement away from 2D culture to 3D culture. Cells grown in 3D are better able to replicate in vivo reality. This is particularly true of hepatocytes. Traditional scaffolds such as alginate, collagen, chitosan, gelatin and polymer scaffolds have all been evaluated, but have significant shortcomings such as weak mechanical properties and poor scaffold morphology.
Self-assembling peptide hydrogels (SAPHs) are attractive alternatives to traditional scaffolds. Attempts have been made to culture using RAD16-1, FMOC-capped hydrogels and FEK hydrogels. However, fine-tuning of SAPHs for specific cell lines is required to maximize their value.
In a pre-publication recently made available online, Yu Xin and colleagues at Manchester University starting with the basic PeptiGel® architecture, developed a novel SAPH, named Alpha 7™, specifically for the culture of hepatocytes.
Hydrogels contain a lot of water and have varying degrees of mechanical strength. These attributes are fundamental to supporting 3D culture. But beyond those parameters, the various hydrogels diverge significantly. One of the key strengths of PeptiGel is the ability to modulate the peptide sequence and integrate functional moieties (e.g. RGD) as an inherent part of that sequence. One of the most important criteria, that is sometimes overlooked, is the charge characteristics of a hydrogel.
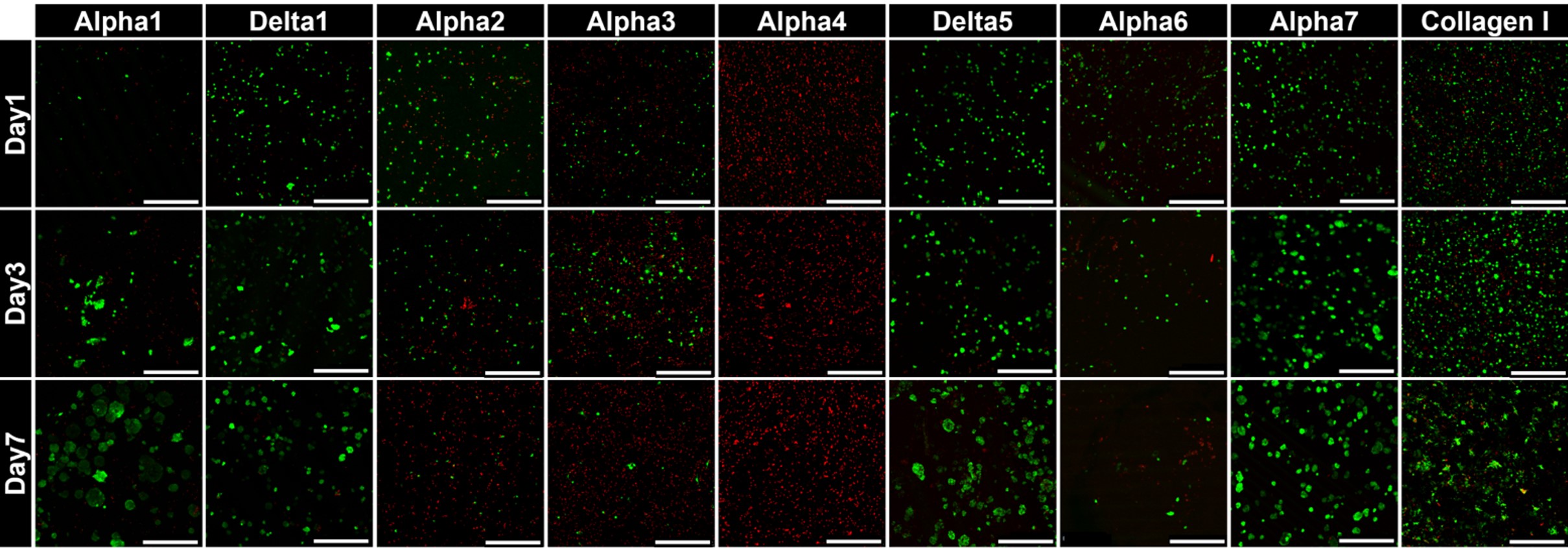
Live (green) dead (red) staining of HegG2 cells grown over 14 days in various hydrogels. Data from Yu Xin et al
Alpha 7 outperforms
Building on previous observations that Delta 5, a negatively charged hydrogel, best-supported culture (proliferation and viability) of hepatocytes when compared with positively charged hydrogels, Alpha 7 was prepared with similar properties to Delta 5 but a slightly reduced charge.
In terms of cell culture viability, Alpha 7 performed better than the other PeptiGels, but only about as well collagen, which is very widely used for hepatocyte culture. The research team started to look closer at Alpha 7, comparing it against collagen. In every respect, Alpha 7 performed as well as, if not better than collagen. Alpha 7 produced spheroids with much great consistency. Albumin was produced by cells grown in Alpha 7 at 4-fold higher rates. Albumin production continued to increase with Alpha 7 throughout the 14-day period of evaluation. Similarly, levels of Urea production in Alpha 7-supported cells were higher. Compared to collagen, Alpha 7 generated more E-cadherin, laminin, F-actin and fibronectin.
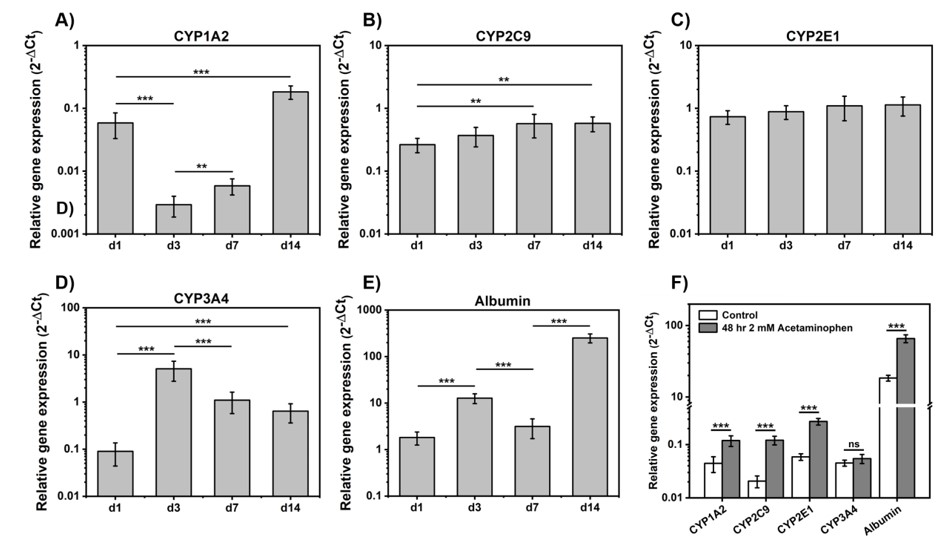
(A-E) CYP and albumin expression in Alpha 7 supported cells over 14 days (F) Expression of CYP genes following paracetemol exposure. Data from Yu Xin et al
Alpha 7 and collagen were then assessed with hepatocytes over a 14-day culture period, during which the ability of the cells to metabolize paracetamol was assessed. The expression of several key CYP450 enzymes (CYP3A4, CYP2C9, CYP1A2 and CYP2E1) involved in drug metabolism was evaluated. In each case, expression levels out-performed collagen with the studies showing Alpha 7 significantly extending the duration of utility for the cells.
7 key ways Alpha 7 boosts Hepatocytes
- Rounder, more uniform spheroids
- Higher albumin levels
- Higher fibronectin levels
- Higher laminin levels
- Higher E-cadherin levels
- Higher CYP levels
- More durable CYP levels
Cell Guidance Systems will introduce Alpha 7, the newest member of the PeptiGel family in the near future.
IMAGE: Live dead staining of hepatocytes with various PeptiGels and collagen. CREDIT Yu Xin et al
Learn more about powerful technologies that are enabling research: