Covid 19: Cytokines' role in the development of lung fibrosis
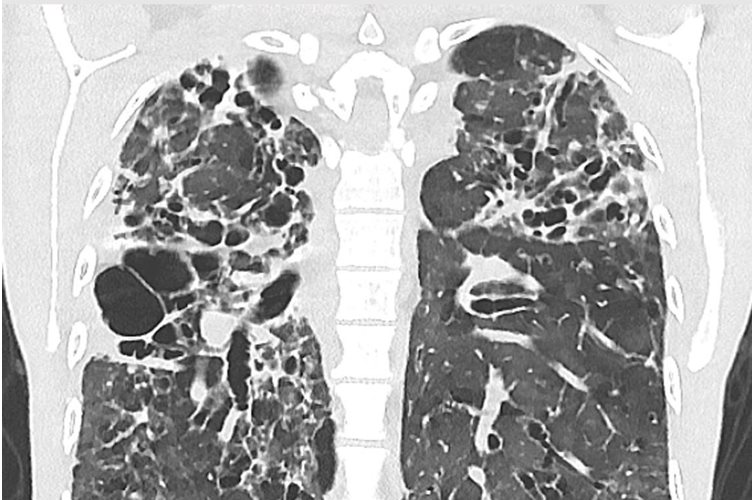
The long-term effects of disease and injury can arise from the body's efforts to regenerate damaged tissue. Scarring of the skin is one example. Internal scarring of tissue can also occur which can lead to more than superficial effects. In Covid 19 and other airway infections, pulmonary fibrosis, driven by cytokines, can have serious implications.