The inkjet set: 3D bioprinting has travelled far
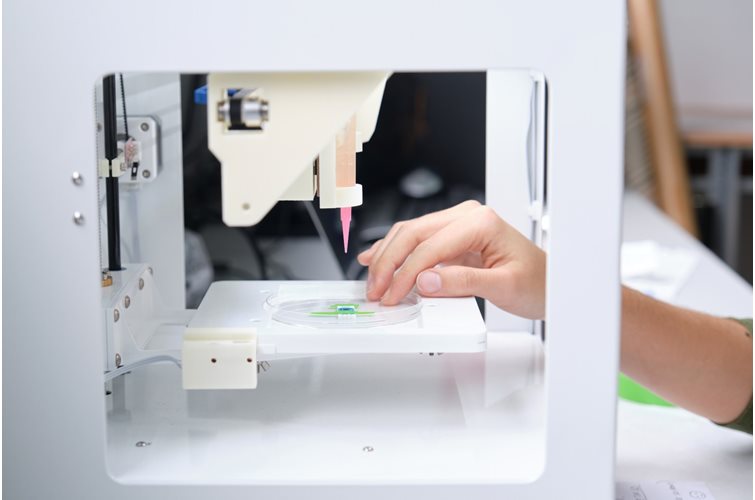

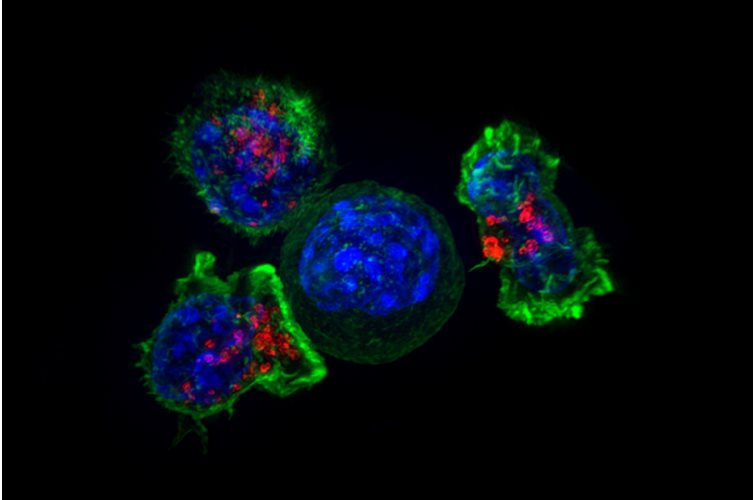
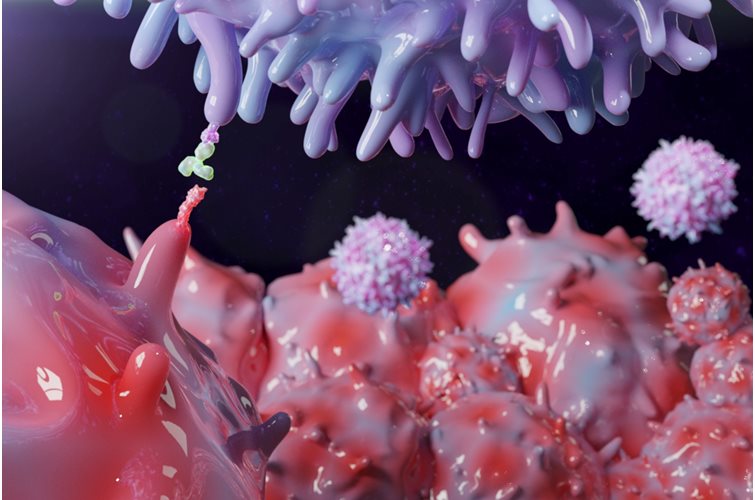
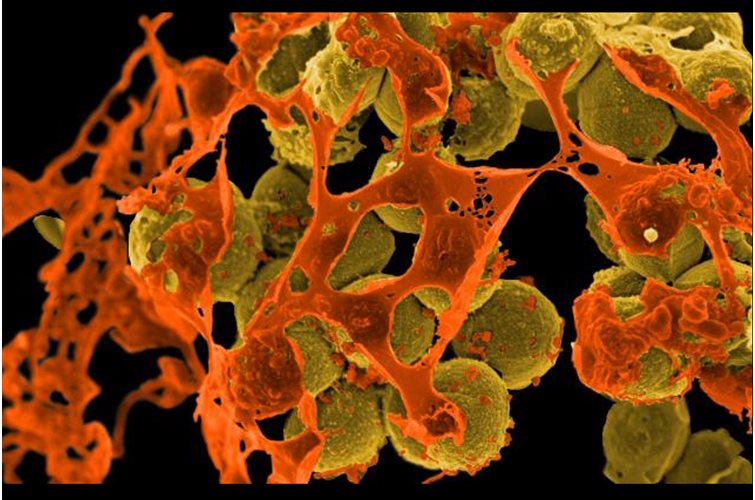
3D bioprinting enables the production of cell-laden models in which cells, biomolecules and biomaterials are deposited in a spatially predefined 3D position. As 3D bioprinting capabilities become more sophisticated, the potential to fabricate functional tissues and organs for drug testing and transplantation is being realized. But with simple stem cell procedures costing $5,000 to $50,000, how many will be able to afford these innovations?